dolution
dolution.
Diet and Birth Weight An obstetrician wanted to determine the impact that three experimental diets had on the birth weights of pregnant mothers. She randomly selected 27 pregnant mothers in the first trimester of whom 9 were 20 to 29 years old, 9 were 30 to 39 years old, and 9 were 40 or older. For each age group, she randomly assigned the mothers to one of the three diets. After delivery, she measured the birth weight (in grams) of the babies and obtained the following data:
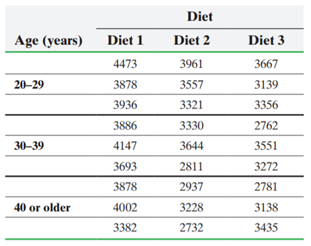
(a) Birth weights are known to be approximately normally distributed. Verify the requirement of equal population variances.
(b) Determine whether there is significant interaction between age and diet.
(c) If there is no significant interaction, determine whether there is significant difference in the means for the three age groups. If there is no significant interaction, determine whether there is significant difference in the means for the diets.
(d) Draw an interaction plot of the data to support the results of parts (b) and (c).
(e) If there is significant difference in the means for the three age groups, use Tukeyââ¬â¢s test to determine which pairwise means differ using a familywise error rate of ![]() . If there is significant difference in the means for the diets, use Tukeyââ¬â¢s test to determine which pairwise means differ using a familywise error rate of
. If there is significant difference in the means for the diets, use Tukeyââ¬â¢s test to determine which pairwise means differ using a familywise error rate of ![]() .
.
"Looking for a Similar Assignment? Get Expert Help at an Amazing Discount!"


